About Net Interest Margin Calculator (Formula)
The Net Interest Margin (NIM) Calculator is an essential tool for banks and financial institutions to evaluate their profitability. NIM is a key performance indicator that measures the difference between the interest income generated and the amount of interest paid out relative to their average earning assets. Understanding and optimizing NIM helps institutions assess their financial health, manage their interest rate risk, and make informed lending decisions.
Formula
The formula for calculating Net Interest Margin is:
NIM = (Total Return – Total Interest Paid) / Average Assets
Where:
- NIM = Net Interest Margin
- Total Return = Total interest income generated from loans and investments
- Total Interest Paid = Interest expenses on deposits and borrowings
- Average Assets = Average earning assets during a specified period
How to Use
Using the Net Interest Margin Calculator is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Gather Required Data: Collect the necessary figures: total return, total interest paid, and average assets for the period under review.
- Input Values: Enter these values into the respective fields in the calculator.
- Calculate NIM: Click the calculate button. The calculator will process your input and display the net interest margin.
Example
Let’s illustrate the calculation with an example. Assume a financial institution has the following data for a fiscal year:
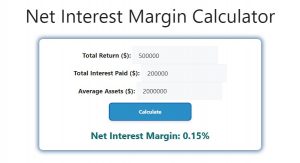
- Total Return: $500,000
- Total Interest Paid: $200,000
- Average Assets: $2,000,000
Using the formula:
NIM = (Total Return – Total Interest Paid) / Average Assets
NIM = ($500,000 – $200,000) / $2,000,000
NIM = $300,000 / $2,000,000
NIM = 0.15 or 15%
In this example, the net interest margin is 15%, indicating that the institution retains 15 cents of every dollar of assets as net interest income.
FAQs
- What does Net Interest Margin (NIM) indicate?
NIM reflects how effectively a financial institution is generating income from its assets relative to its interest expenses. - Why is NIM important for banks?
It helps banks assess their profitability and efficiency in managing interest rate risk. - What is considered a good NIM?
A higher NIM indicates better profitability, but what is “good” can vary by institution and market conditions. - How often should NIM be calculated?
NIM should be calculated regularly, typically quarterly or annually, to track performance trends. - Can NIM be negative?
Yes, a negative NIM occurs when interest expenses exceed interest income, indicating a loss. - What factors can affect NIM?
Interest rates, loan-to-deposit ratios, and market competition can significantly influence NIM. - How can a bank improve its NIM?
By increasing interest income, reducing interest expenses, or optimizing asset allocation. - Does NIM account for non-interest income?
No, NIM specifically focuses on interest income and expenses and does not include fees or commissions. - Is NIM the same as profit margin?
No, profit margin considers total revenues and expenses, while NIM is specific to interest-related income. - How do changes in interest rates affect NIM?
Rising interest rates can increase interest income if loans are priced accordingly, but can also increase interest expenses on deposits. - What role does asset quality play in NIM?
Higher quality assets tend to generate more consistent interest income, positively impacting NIM. - Can NIM be used to compare banks?
Yes, comparing NIM across similar institutions can provide insights into operational efficiency and profitability. - What are average assets?
Average assets are calculated by averaging the beginning and ending asset values over a period. - How does a bank’s lending strategy affect NIM?
A focus on higher-yielding loans can improve NIM, while an emphasis on lower-risk loans may lower NIM. - What is the impact of competition on NIM?
Increased competition may pressure banks to lower interest rates on loans, potentially reducing NIM. - Are there any limitations to using NIM?
NIM does not provide a complete picture of a bank’s overall profitability or operational efficiency. - How do financial crises affect NIM?
Economic downturns can lead to higher loan defaults and lower interest income, negatively impacting NIM. - What other metrics should be considered alongside NIM?
Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) are important complementary metrics. - Can NIM be used for non-bank financial institutions?
Yes, NIM is relevant for any institution that generates interest income and incurs interest expenses. - How do banks report NIM?
NIM is typically reported in financial statements or regulatory filings as part of financial performance metrics.
Conclusion
The Net Interest Margin Calculator is a powerful tool for financial institutions to evaluate their profitability and operational efficiency. By accurately calculating NIM, banks can make informed decisions to optimize their interest income and manage their interest rate risks. Regular monitoring of NIM helps organizations understand their financial health and improve their strategic planning for sustainable growth.
