About Muscle to Fat Ratio Calculator (Formula)
A muscle to fat ratio calculator helps determine the balance between muscle mass and fat mass in your body. This ratio is an important metric in assessing physical fitness and body composition, as it provides insights into whether you need to focus on building muscle or reducing fat. The higher the muscle to fat ratio, the healthier and fitter your body tends to be.
Formula
The formula to calculate muscle to fat ratio is:
Muscle to Fat Ratio = Muscle Mass / Fat Mass
Where:
- Muscle Mass: The total weight of muscles in your body
- Fat Mass: The total weight of fat in your body
How to Use
- Measure your muscle mass: You can use a body composition scale or DEXA scan to accurately measure muscle mass.
- Measure your fat mass: Use the same tools or other methods like skinfold calipers to measure fat mass.
- Input your values: Enter the muscle mass and fat mass into the calculator.
- Calculate the ratio: The calculator will divide the muscle mass by fat mass to give you your muscle to fat ratio.
Example
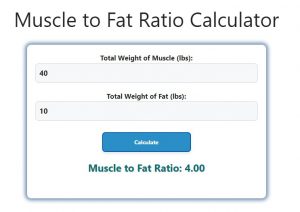
Suppose you have a muscle mass of 40 kg and a fat mass of 10 kg. Using the formula:
Muscle to Fat Ratio = 40 / 10
Muscle to Fat Ratio = 4
This means for every unit of fat, you have 4 units of muscle, which indicates a healthy body composition.
FAQs
- What is a muscle to fat ratio?
The muscle to fat ratio is the proportion of muscle mass to fat mass in the body, which helps assess overall fitness and body composition. - How is muscle to fat ratio calculated?
It is calculated by dividing the total muscle mass by the total fat mass in your body. - Why is muscle to fat ratio important?
This ratio provides a better understanding of your body composition and helps in creating fitness goals, whether to build muscle or lose fat. - What is a good muscle to fat ratio?
A higher ratio generally indicates a healthier and more fit body. The ideal ratio can vary depending on age, gender, and fitness levels. - Can you improve your muscle to fat ratio?
Yes, by increasing muscle mass through strength training and reducing fat through diet and cardio, you can improve your muscle to fat ratio. - Does age affect muscle to fat ratio?
Yes, as you age, muscle mass naturally declines, and fat tends to increase, which can lower your muscle to fat ratio. - Is the muscle to fat ratio the same for men and women?
No, men generally have a higher muscle to fat ratio than women due to differences in body composition and hormonal levels. - How can I measure muscle mass?
You can measure muscle mass using body composition scales, DEXA scans, or bioelectrical impedance devices. - How can I measure fat mass?
Fat mass can be measured using body fat scales, skinfold calipers, or DEXA scans. - Can I improve muscle to fat ratio without losing weight?
Yes, it’s possible to improve the ratio by building muscle while maintaining or slightly increasing your weight, as long as fat mass decreases. - What happens if my muscle to fat ratio is too low?
A low muscle to fat ratio may indicate an excess of body fat relative to muscle, which can negatively impact physical health and fitness. - Can cardio help improve my muscle to fat ratio?
Yes, cardio can help burn fat, improving your muscle to fat ratio, especially when combined with strength training. - What role does diet play in the muscle to fat ratio?
A diet rich in protein and balanced in nutrients helps support muscle growth, while managing calorie intake can reduce fat mass. - What’s the difference between muscle to fat ratio and body mass index (BMI)?
BMI only considers overall weight and height, while muscle to fat ratio specifically measures the proportion of muscle to fat, providing more detailed body composition information. - How often should I calculate my muscle to fat ratio?
It’s recommended to track your ratio every few months, especially if you are working on specific fitness goals. - Does muscle weigh more than fat?
Muscle is denser than fat, meaning it takes up less space in the body, but one kilogram of muscle weighs the same as one kilogram of fat. - Can women have a high muscle to fat ratio?
Yes, with strength training and a balanced diet, women can achieve a high muscle to fat ratio. - Is muscle to fat ratio more accurate than body fat percentage?
Both metrics are valuable, but muscle to fat ratio gives a clearer picture of how much of your body weight is made up of muscle versus fat. - Can this ratio impact metabolism?
Yes, a higher muscle mass increases your metabolism because muscle burns more calories at rest than fat. - How does muscle to fat ratio affect athletic performance?
A higher muscle to fat ratio generally enhances strength, endurance, and overall athletic performance.
Conclusion
The muscle to fat ratio calculator is an essential tool for assessing your body composition and overall health. By understanding your muscle to fat ratio, you can tailor your fitness and nutrition plan to achieve your health goals. Regularly checking this ratio can help you maintain a balanced and healthy body composition over time.