About Diversion Rate Calculator (Formula)
A Diversion Rate Calculator is a useful tool to measure the percentage of waste that is diverted from landfills through recycling, composting, or reuse efforts. It helps organizations, businesses, and households understand their waste management efficiency and track sustainability goals. The higher the diversion rate, the better the waste is being managed by reducing landfill usage and enhancing recycling efforts.
Formula
The formula to calculate the diversion rate is as follows:
Diversion Rate (%) = (Weight of Diverted Waste / Weight of Total Waste) * 100
Where:
- Weight of Diverted Waste is the total amount of waste that is recycled, composted, or reused.
- Weight of Total Waste is the sum of diverted waste plus the waste sent to the landfill.
How to Use
- Collect Data: Measure or gather the total weight of all waste produced, including the waste sent to landfills and the waste diverted (recycled or reused).
- Apply the Formula: Divide the weight of diverted waste by the total weight of waste, and multiply the result by 100 to get the diversion rate percentage.
- Interpret the Result: The higher the percentage, the better your waste management is, as more waste is being diverted from landfills.
Example
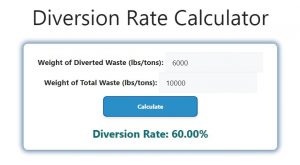
Let’s say a company generates 10,000 kilograms of total waste in a month. Out of this, 6,000 kilograms of waste is recycled or composted. Using the formula:
Diversion Rate (%) = (6,000 kg / 10,000 kg) * 100
Diversion Rate (%) = 60%
This means that 60% of the company’s waste was diverted from landfills through recycling or composting.
FAQs
- What is a Diversion Rate Calculator?
A Diversion Rate Calculator is a tool used to determine the percentage of waste that is diverted from landfills to recycling, composting, or reuse. - Why is it important to calculate diversion rates?
Calculating diversion rates helps track waste management performance, assess sustainability efforts, and reduce environmental impacts by diverting waste from landfills. - What is considered diverted waste?
Diverted waste includes materials that are recycled, composted, reused, or otherwise prevented from being sent to landfills or incineration. - What is a good diversion rate?
A good diversion rate varies by industry, but many organizations aim for 50% or higher, with some targeting zero waste (100% diversion). - How can I improve my diversion rate?
To improve your diversion rate, increase recycling programs, compost organic waste, reuse materials, and reduce overall waste generation. - Is composting included in the diversion rate?
Yes, composting is considered part of diverted waste because it keeps organic materials out of landfills. - What is total waste in the diversion rate formula?
Total waste is the sum of all waste generated, including both the diverted waste and the waste sent to landfills or other disposal methods. - Can businesses use a Diversion Rate Calculator?
Yes, businesses use Diversion Rate Calculators to measure their waste management performance and align with sustainability goals. - How is the weight of waste measured?
Waste weight is typically measured in kilograms or pounds, depending on the standard used in the region or by the organization. - What industries benefit most from calculating diversion rates?
Industries like manufacturing, retail, and construction benefit greatly from calculating diversion rates to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulations. - Can households use a Diversion Rate Calculator?
Yes, households can use a Diversion Rate Calculator to track recycling efforts and reduce waste sent to landfills. - What happens if the diversion rate is low?
A low diversion rate indicates that a large portion of waste is going to landfills, meaning there is room for improvement in recycling and waste management efforts. - What types of materials contribute to a higher diversion rate?
Materials such as paper, plastic, metal, glass, and organic waste contribute to a higher diversion rate when they are recycled or composted. - Does waste-to-energy count as diversion?
This depends on regional regulations. In some areas, waste-to-energy (incineration with energy recovery) may count toward diversion rates, but in others, it does not. - What is the difference between diversion and recycling?
Diversion includes all methods of keeping waste out of landfills, such as recycling, composting, and reuse, while recycling specifically refers to reprocessing materials into new products. - What is zero waste?
Zero waste is a philosophy and goal that encourages the redesign of resource life cycles so that all products are reused, and no trash is sent to landfills or incinerators. - How often should I calculate my diversion rate?
Diversion rates can be calculated monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on how often you want to track your waste management progress. - Can I compare my diversion rate with others?
Yes, diversion rates can be compared between businesses, cities, or industries to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. - What tools can help with waste management?
In addition to a Diversion Rate Calculator, tools like waste audits, recycling programs, and sustainability tracking software can help with effective waste management. - How can diversion rates contribute to sustainability goals?
Higher diversion rates reduce the amount of waste going to landfills, conserve resources, and lower greenhouse gas emissions, all of which contribute to sustainability goals.
Conclusion
The Diversion Rate Calculator is an essential tool for tracking the efficiency of waste management practices. By using the formula to calculate the percentage of waste diverted from landfills, businesses and individuals can assess and improve their recycling and composting efforts. Understanding and applying diversion rates helps reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and work towards a sustainable future.