About Variable Cost Ratio Calculator (Formula)
A Variable Cost Ratio Calculator is a useful tool for determining the proportion of variable costs in relation to total revenue. By calculating the variable cost ratio, businesses can analyze how much of their revenue goes toward covering costs that fluctuate with production. This ratio plays a critical role in cost management and financial planning.
Formula
The formula for calculating the variable cost ratio is:
Variable Cost Ratio = (Total Variable Costs / Net Revenue) * 100%
This formula helps you determine the percentage of revenue used to cover variable costs, allowing you to assess cost efficiency.
How to Use
To use the Variable Cost Ratio Calculator, follow these steps:
- Gather Total Variable Costs: Add up all costs that change with production volume, such as raw materials, direct labor, and packaging.
- Determine Net Revenue: Calculate total sales revenue minus any discounts or returns.
- Apply the Formula: Divide total variable costs by net revenue and multiply by 100% to get the variable cost ratio as a percentage.
- Interpret the Result: A higher ratio means a larger portion of revenue is spent on variable costs, which may indicate lower profitability.
Example
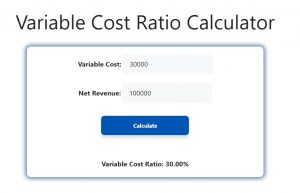
Let’s say a business has total variable costs of $30,000 and net revenue of $100,000. The variable cost ratio is calculated as:
Variable Cost Ratio = ($30,000 / $100,000) * 100% = 30%
This means 30% of the company’s revenue is used to cover variable costs, and the remaining 70% is available to cover fixed costs and profit.
FAQs
- What is the variable cost ratio?
The variable cost ratio measures the percentage of revenue that goes toward covering variable costs, which change based on production levels. - Why is the variable cost ratio important?
It helps businesses understand how much of their revenue is consumed by costs that fluctuate with production, allowing for better financial planning. - What are examples of variable costs?
Examples include raw materials, direct labor, commissions, packaging, and utilities that vary with production output. - How does the variable cost ratio affect profitability?
A lower variable cost ratio means more revenue is available for fixed costs and profit, while a higher ratio indicates higher variable costs relative to revenue. - What is the difference between variable and fixed costs?
Variable costs change with production volume, while fixed costs remain constant regardless of output. - Can the variable cost ratio change over time?
Yes, the ratio can fluctuate as variable costs and net revenue change due to production volume, pricing, or cost management. - How do you reduce the variable cost ratio?
Businesses can lower the ratio by reducing variable costs or increasing net revenue through efficient production or better pricing strategies. - Is a high variable cost ratio bad for business?
A high variable cost ratio can indicate that too much revenue is being consumed by variable expenses, leaving less for profit and fixed costs. - What industries typically have high variable cost ratios?
Industries with high variable costs, such as manufacturing, retail, and agriculture, often see higher variable cost ratios. - Can a business have a negative variable cost ratio?
No, since variable costs cannot exceed net revenue without the business incurring a loss, the ratio cannot be negative. - How often should businesses calculate the variable cost ratio?
Businesses should calculate this ratio regularly, especially after changes in production levels, pricing, or variable cost structures. - What happens if the variable cost ratio is too high?
A high ratio may indicate inefficiencies, and businesses may need to find ways to reduce variable costs or boost revenue. - Can a company control its variable cost ratio?
Yes, by managing production processes, negotiating supplier prices, or optimizing sales strategies, companies can influence their variable cost ratio. - What role does sales volume play in the variable cost ratio?
Sales volume affects both variable costs and net revenue, impacting the overall ratio. Higher sales can lead to a lower ratio if fixed costs are spread over more units. - How does inflation affect the variable cost ratio?
Inflation can increase variable costs, leading to a higher variable cost ratio unless businesses can raise prices or improve cost efficiency. - What is a good variable cost ratio?
There’s no universal benchmark; it depends on industry standards and business goals. Generally, a lower ratio is better as it indicates greater profitability. - How does the variable cost ratio differ from contribution margin?
While the variable cost ratio shows the proportion of revenue consumed by variable costs, the contribution margin shows how much revenue remains after covering variable costs. - Can technology help in reducing the variable cost ratio?
Yes, automation and advanced production techniques can lower variable costs by reducing labor, waste, and inefficiencies. - What is the impact of a changing product mix on the variable cost ratio?
Different products have different variable costs, so a shift in product mix can change the overall ratio based on the cost structure of each product. - How does pricing affect the variable cost ratio?
Increasing prices without increasing variable costs can lower the variable cost ratio by boosting net revenue.
Conclusion
The Variable Cost Ratio Calculator is a vital tool for businesses to track how much of their revenue goes toward variable costs. Understanding this ratio can help companies manage costs, optimize production, and improve profitability. Regularly calculating the variable cost ratio allows businesses to monitor financial health and make informed decisions to achieve long-term success.